quantitative sampling procedure|sampling frame in quantitative research : white label First, you need to understand the difference between a population and a sample, and identify the target population of your research. 1. The populationis the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about. 2. The sampleis the specific group of individuals that you will collect data from. The population can be . See more webParty of Five (1994–2000) Full Cast & Crew. See agents for this cast & crew on IMDbPro. Series Directed by. Steven Robman. . (22 episodes, 1994-2000) Ken Topolsky. . (19 episodes, 1994-2000) Daniel Attias. . (17 episodes, 1995-2000) Michael Engler. . (15 episodes, 1994-1998) Ellen S. Pressman. . (10 episodes, 1994-1999) Lou Antonio. .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 15 de jul. de 2021 · American Horror Stories estreou hoje no Hulu com seus dois primeiros episódios. A série é derivada da série principal American Horror Story e ao invés de .
First, you need to understand the difference between a population and a sample, and identify the target population of your research. 1. The populationis the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about. 2. The sampleis the specific group of individuals that you will collect data from. The population can be . See more
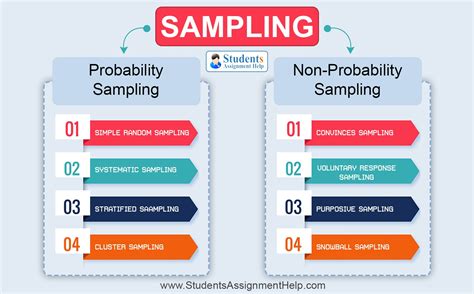
Probability sampling means that every member of the population has a chance of being selected. It is mainly used in quantitative research. If you want to produce results that . See more
In a non-probability sample, individuals are selected based on non-random criteria, and not every individual has a chance of being included. This type of sample is easier and cheaper to access, but it has a higher risk of sampling bias. That means the inferences you . See more
If you want to know more about statistics, methodology, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples. See more
The sampling process involves choosing people, and it is distinct from the sample. 40 In quantitative research, the sample must accurately reflect the target population, be free from .
In quantitative research, collecting data from an entire population of a study is impractical in many instances. It squanders resources like time and money which can be .Researchers focus on the specific techniques that will yield highly representative samples (i.e., samples that are very much like the population). Quantitative researchers tend to use a type of . This article reviews probability and non-probability sampling methods, lists and defines specific sampling techniques, and provides pros and cons for consideration. In . This tutorial will introduce sampling methods and potential sampling errors to avoid when conducting medical research. Contents. Introduction to sampling methods; Examples of different sampling methods; .
The sampling technique in quantitative research comes from its ability to draw small units of the population (i.e., sample size) and generalize it to the population (Seddon & Scheepers, 2012).Probability-based sampling methods are most commonly used in quantitative research, especially when it’s important to achieve a representative sample that allows the researcher to generalise their findings. First, you need to understand the difference between a population and a sample, and identify the target population of your research. The population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about. The sample is the .
Knowledge of sampling methods is essential to design quality research. Critical questions are provided to help researchers choose a sampling method. This article reviews probability and non-probability sampling methods, lists and defines specific sampling techniques, and provides pros and cons for consideration. Sampling Methods in Research Methodology; How to Choose a Sampling Technique for Research . The quantitative data revealed that administrative staff use company internet and computers to perform .You might remember studying sampling in a quantitative research course. Sampling is important here too, but it works a bit differently. Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research involves nonprobability sampling. This chapter .Simple random sampling. Simple random sampling involves selecting participants in a completely random fashion, where each participant has an equal chance of being selected.Basically, this sampling method is the equivalent of pulling names out of a hat, except that you can do it digitally.For example, if you had a list of 500 people, you could use a random .
There are two broad classes of sampling in quantitative research: Probability and nonprobability sampling. Probability sampling: . Common Data Collection Methods in Quantitative Research. There are various methods that researchers use to collect data for their studies. For nurse researchers, existing records are an important data source.
digital refractometer drawing
Quantitative research is more systematic and controlled than qualitative. However, both research methods have a statement of the problem to investigate. At this point, it is . sampling procedure, data gathering, and data analysis. Each research type also aims to answer specific research questions; how it will be answered is determined by its .
Researchers use surveys, experiments, and other quantitative methods to collect data that can inform social policies, educational programs, and community interventions. Education Research: . This is achieved through the use of random sampling methods and statistical inference. Examples of Quantitative Research. Quantitative researchers are often interested in being able to make generalizations about groups larger than their study samples. While there are certainly instances when quantitative researchers rely on nonprobability samples (e.g., when doing exploratory or evaluation research), quantitative researchers tend to rely on probability sampling techniques.
types of quantitative sampling techniques
Quantitative researchers are often interested in being able to make generalizations about groups larger than their study samples. While there are certainly instances when quantitative researchers rely on nonprobability samples (e.g., when doing exploratory or evaluation research), quantitative researchers tend to rely on probability sampling techniques. Introduction. Sampling is a critical, often overlooked aspect of the research process. The importance of sampling extends to the ability to draw accurate inferences, and it is an integral part of qualitative guidelines across research methods. Probability sampling. Unlike nonprobability sampling, probability sampling refers to sampling techniques for which a person’s likelihood of being selected from the sampling frame is known. You might ask yourself why we should care about a potential participant’s likelihood of being selected for the researcher’s sample.
Non-probability sampling methods are those in which elements are chosen through non-random methods for inclusion into the research study and include convenience sampling, purposive sampling, and . When to use purposive sampling. Purposive sampling is best used when you want to focus in depth on relatively small samples.Perhaps you would like to access a particular subset of the population that shares certain characteristics, or you are researching issues likely to have unique cases.. The main goal of purposive sampling is to identify the cases, individuals, .There are two main sampling methods for quantitative research: Probability and Non-probability sampling.. Probability sampling. A theory of probability is used to filter individuals from a population and create samples in probability sampling.Participants of a sample are chosen by random selection processes. Probability sampling
What Is Non-Probability Sampling? | Types & Examples. Published on July 20, 2022 by Kassiani Nikolopoulou.Revised on June 22, 2023. Non-probability sampling is a sampling method that uses non-random criteria like the availability, geographical proximity, or expert knowledge of the individuals you want to research in order to answer a research question. We could choose a sampling method based on whether we want to account for sampling bias; a random sampling method is often preferred over a non-random method for this reason. Random sampling examples include: .Chapter Outline. The sampling process (25 minute read); Sampling approaches for quantitative research (15 minute read); Sample quality (24 minute read); Content warning: examples contain references to addiction to technology, domestic violence and batterer intervention, cancer, illegal drug use, LGBTQ+ discrimination, binge drinking, intimate partner violence among college .
Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method in which researchers select members of the population at a regular interval (or k) determined in advance. If the population order is random or random-like (e.g., alphabetical), then this method will give you a representative sample that can be used to draw conclusions about your population of . Predetermined variables and measurement procedures can mean that you ignore other relevant observations. Structural bias; Despite standardized procedures, structural biases can still affect quantitative research. Missing data, imprecise measurements or inappropriate sampling methods are biases that can lead to the wrong conclusions. Lack of contextChapter Outline. The sampling process (25 minute read); Sampling approaches for quantitative research (15 minute read); Sample quality (24 minute read); Content warning: examples contain references to addiction to technology, domestic violence and batterer intervention, cancer, illegal drug use, LGBTQ+ discrimination, binge drinking, intimate partner violence among college .
The research utilized a quantitative-correlation design involving 1,494 respondents selected through simple random sampling. . The sampling method is significant to strengthen the . Graduate Research Methods in Social Work (DeCarlo, Cummings, and Agnelli) 10: Using quantitative methods - Quantitative sampling 10.2: Sampling approaches for quantitative research . Sampling in quantitative research projects is done because it is not feasible to study the whole population, and researchers hope to take what we learn about a . Non-probability Sampling Methods. Another class of sampling methods is known as non-probability sampling methods because not every member in a population has an equal probability of being selected to be in the sample. This type of sampling method is sometimes used because it’s much cheaper and more convenient compared to probability .
Survey is a method of collecting large scale quantitative data, but it does not us e. an experimental design. . Sampling methods can be categorized according to the approach they take to the .
SAMPLING. Sampling can be defined as the process through which individuals or sampling units are selected from the sample frame. The sampling strategy needs to be specified in advance, given that the sampling method may affect the sample size estimation. 1,5 Without a rigorous sampling plan the estimates derived from the study may be biased (selection bias). 3
3. Snowball Sampling. Snowball sampling, also called referral sampling, is a unique approach researchers use to recruit participants in qualitative research. The technique involves identifying a few initial participants who meet the eligibility criteria and asking them to refer others they know who also fit the requirements.
types of quantitative sampling methods
simple random sampling methods
Resultado da Loja objetiva. Centro, Rio das Ostras - RJ, 28890-000, Brasil. Aparência. Fotos. Comentários. Informações. Horário de trabalho. Serviços. .
quantitative sampling procedure|sampling frame in quantitative research